Word File Formats:
PDF File Formats:
Another Download link from docplayer:
https://docplayer.net/221923721-Basketball-basic-technical-training-course-project-research.html
Stay with science and knowledge.
Fulfilled With Space !

Another Download link from docplayer:
https://docplayer.net/221923721-Basketball-basic-technical-training-course-project-research.html
Stay with science and knowledge.
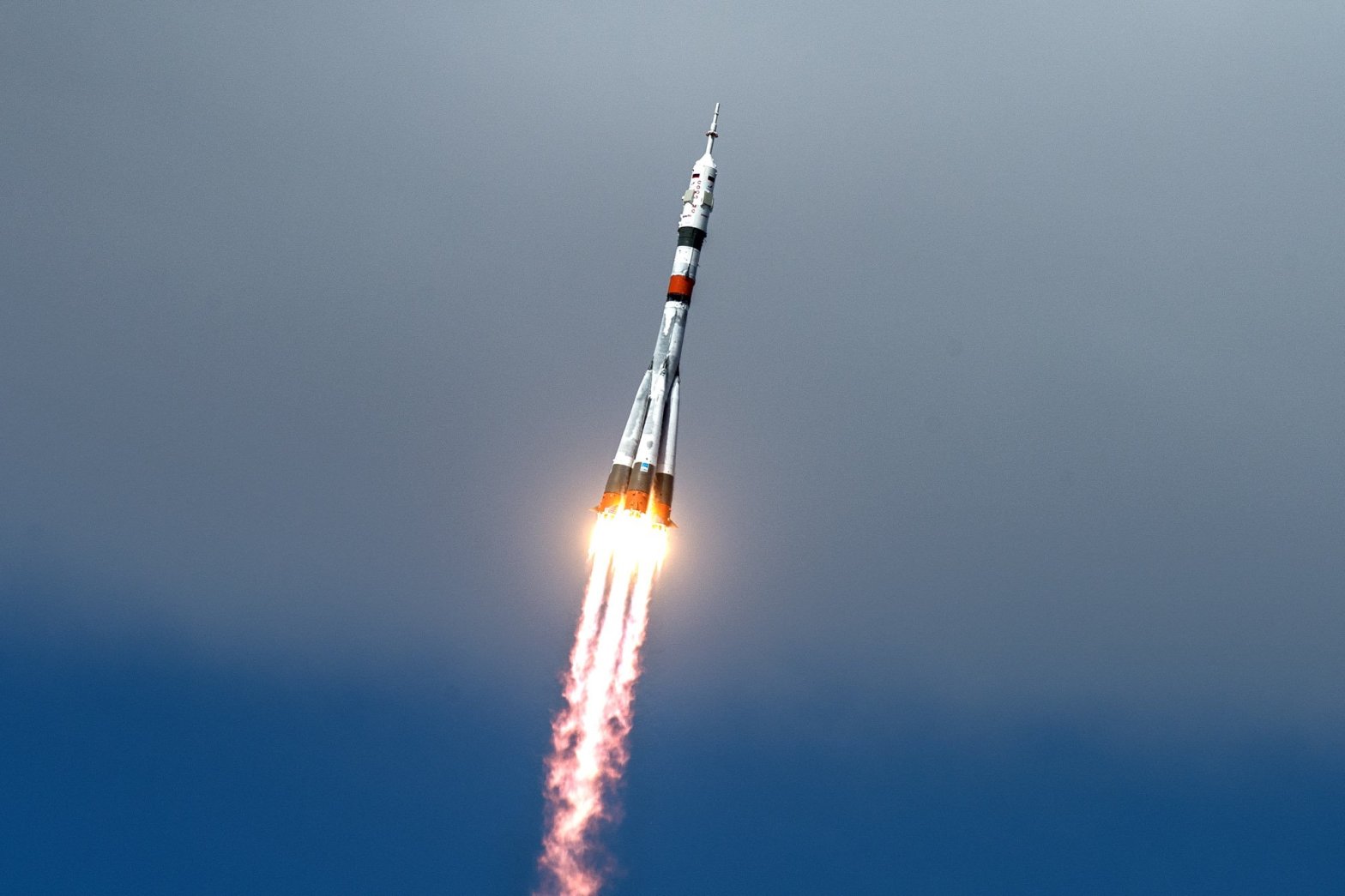

A hybrid-fuel rocket is a rocket using different rocket fuels in different phases in the rocket engine. One of these fuels is in solid form and the other is in gas or liquid form. The emergence of the hybrid rocket can be traced back to 1940s.

In its simplest form, a hybrid rocket engine consists of a pressurized boiler (tank) containing liquid oxidizer and a combustion chamber containing solid rocket fuel and a mechanical device that separates them. When propulsion is required, a suitable ignition source is introduced into the combustion chamber and the valve in between is opened. Liquid (or gas) fuel flows into the combustion chamber and evaporates there, then interacts with the solid fuel. Combustion takes place in a boundary layer propagation flame adjacent to the surface of the solid fuel.
Generally, liquid rocket fuel is used as an oxidizer and solid rocket fuel as fuel because solid oxidizers are very dangerous and are less efficient than liquid oxidizers. In addition, the use of solid fuels such as Hydroxyl Terminated PolyButadiene (HTPB) or paraffin wax makes it possible to add high energy fuel additives such as aluminum, lithium, and metal hydrides.
Hybrid rockets not only overcome the disadvantages of solid propellant rockets, such as the dangers associated with the transport of fuel, but also avoid the disadvantages of liquid propellant rockets, such as the mechanical complexity. Hybrid rockets fail more safely (without explosion) than liquid or solid fuel rockets because it is very difficult to mix the fuel and oxidizer (due to their different states of matter) homogeneously. Like liquid fuel rocket engines, hybrid rocket engines can be easily switched off and their thrust amounts / levels can be adjusted. The theoretical specific impulse efficiency of hybrids is generally higher than solid fuel engines and less than liquid fuel engines. High specific propellant values of up to 400 seconds were measured in hybrid rocket engines using high metal content fuel. Hybrid systems are more complex than solid ones, but because of the separate storage of the oxidizer and fuel, they overcome the significant hazards that can occur during production, long-distance transport / handling, and physical handling / handling.

Apart from these advantages, there are also disadvantages.
1) Low burning rate. Reacting with oxidizer the fuel entering and burning, expected from the rocket. In terms of generating instantaneous force, solid fuel burn more slowly than motors. This is because combustion occurs with the fuel evaporating from the surfaces and this is that evaporation is not fast enough. But in long-term low power needs (target, such as gas generators) this characteristic behavior is important takes a place.
2) Low core density. Multiple fuel core geometry has been the most common method used to avoid low burning rate. Especially in this application made in engines larger than a foot diameter, the density decreases as the fuel is stored in larger volumes. In addition, unburned inert fuels (fuel sliver) remaining at the ends of each separate geometry reduce efficiency.
3) Combustion efficiency. Compared to liquid and solid fuel rocket engines, the combustion efficiency of hybrid engines is 1-2% lower. However, since the specific impulse value is higher compared to solid fuel rocket engines, the effect of efficiency
remains low.
4) Mixing ratio (O / F). As the combustion surface increases during the combustion (the inner diameter of the fuel core gradually increases and reaches the outer diameter), the fuel mixture ratio deviates from the theoretical value in time. But the beginning
This can be overcome with an appropriate ratio chosen for According to internal ballistic calculations, this deviation is below 1%.
5) Slow transition. Response to power-up (ignition, power change, termination) is usually slow. However, this situation can be ignored in practical application where renewability is more important.
Stay with science and knowledge.
SAMUR, A. E., HACIOGLU, A., KARABEYOGLU, A. (2016). Hi̇bri̇t yakitli roket motoru ateşleme/test düzeneği̇ tasarimi. Aerospace Technologies Journal, 9(1), 25-30.
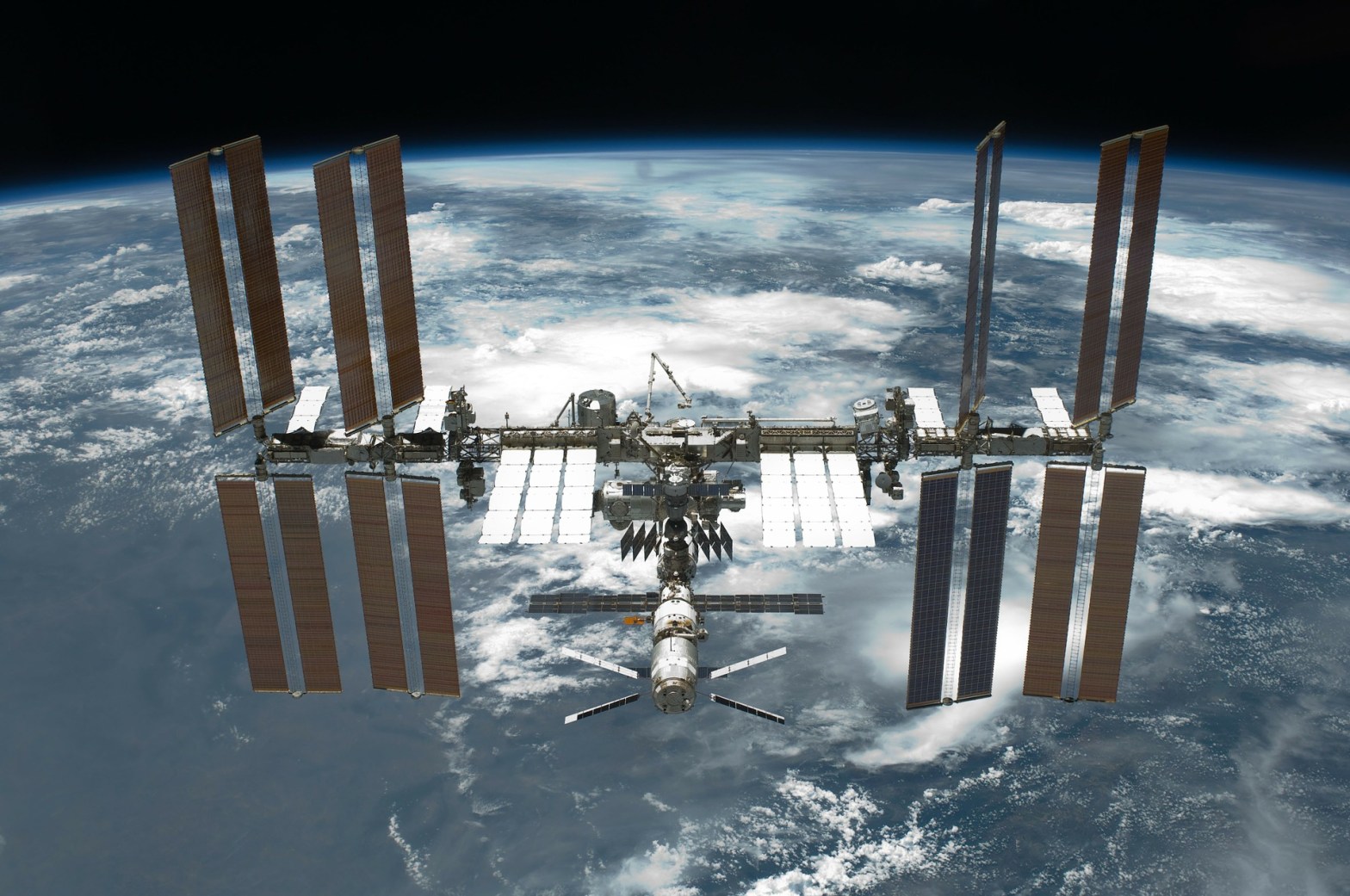

The International Space Station (ISS) is a space base placed in low Earth orbit, in other words, an artificial satellite that can be lived on. The first part of the station, which was built by combining the modules put together, was launched in 1998. The structure of the station basically consists of pressurized modules, supporting exoskeleton and solar panels. It is the largest artificial satellite orbiting the earth. It can be seen with the naked eye when viewed from the earth at appropriate times.
ISS is a laboratory center providing space environment and low gravity environment for experiments. It allows the crew to experiment in biology, physiology, physics, chemistry, astronomy, meteorology, and more. The station also provides a very suitable environment for testing equipment and systems planned for use in Lunar and Mars missions in space before use.
The station, which holds the record for the longest continuous human possession in space, has continuously accommodated and continues to accommodate the space crew for 7275 days since the Recon 1 shuttle arrived at the station on 2 November 2000. The previous record belonged to the Soviet space station Mir with 3644 days. ISS has hosted astronauts and cosmonauts from 15 different nations to date.
The International Space Station program is a joint project created by five participating space organizations, namely the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the Russian Federal Space Agency, the Japan Space Research Agency, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency. Ownership and usage rights of the station are determined by intergovernmental treaties and conventions. The station consists of two parts, the Russian Orbital Division and the United States Orbital Division. The orbital altitude of the station is 330 km. up to 435 km. ranges between. The station uses the engines of the Zvezda module or visitor spacecraft to increase its altitude, which decreases over time. It makes 15.5 turns around the Earth in a day.
As a result of the USA’s budget increase, the station’s term of office has been extended from 2020 to 2024, and it is likely to be extended to 2028. It is still unclear whether countries such as Russia, Germany, France, Japan and Canada, which are currently supporting the project and declaring that they will support the project until 2020, will contribute to this extended budget. The Russian Federal Space Agency has made a bid to build a new station called OPSEK using the station before the International Space Station retires. ISS is the ninth station that has been built to date and accommodates personnel.
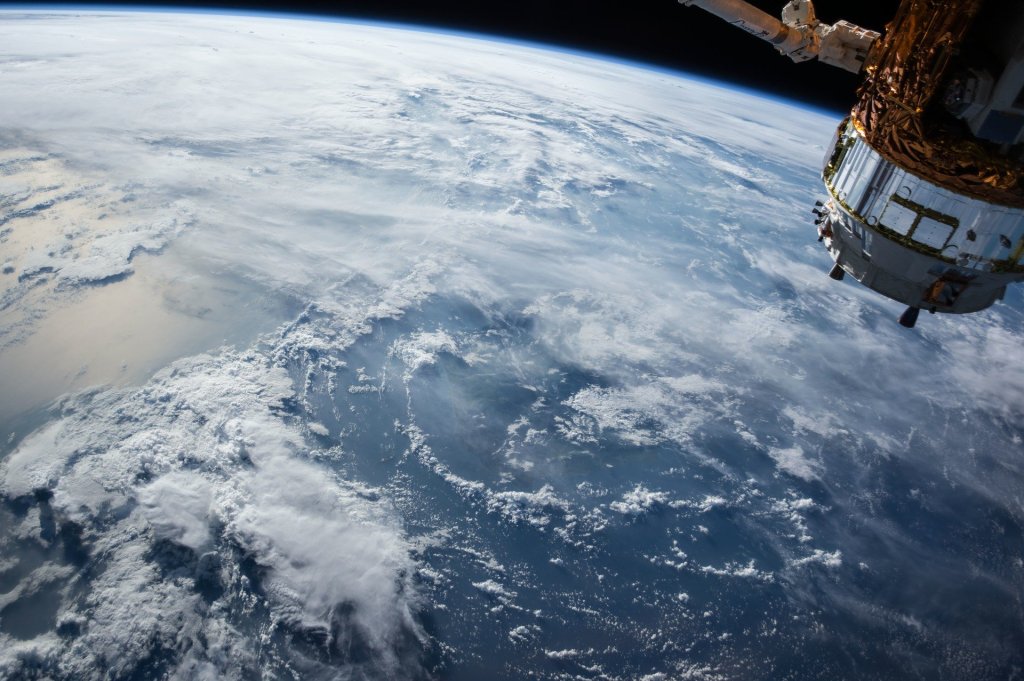

According to the original joint declaration of intent between the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration and the Russian Federal Space Agency, the International Space Station was planned to be a laboratory, observatory and factory. It was also planned to serve as transportation, maintenance and intermediate bases for the future Moon, Mars and various asteroid missions. In the US national space policy for 2010, the Station was given commercial, diplomatic and educational missions in addition to its current missions.
The International Space Station acts as an environment for research that cannot be carried out elsewhere. While small, unmanned spacecraft provide the environment for non-gravity and exposures to space, stations can host experiments that could last for decades. In this way, an environment that can go beyond the capabilities of manned space shuttles is created.
The International Space Station is affected by Earth’s gravity. Although gravity is less than the earth’s surface, it is not zero. But since the station is in continuous motion in orbit, gravity is balanced by centrifugal force. Researchers examine the effects of this near-weightless environment on development, growth, evolution and constitutive functions. NASA wants to do research on how 3D humanoid tissues are formed in microgravity.
As a result, ISS has performed great services on behalf of humanity in the process from its launch until today, and it still does. This project has been one of the best examples of what many nations have come together to achieve when the subject is science and research. The surplus that science and technology adds to the human race does not end and humanity develops as it develops.
Stay with science and knowledge.
^ “Central Research Institute for Machine Building (FGUP TSNIIMASH) Control of manned and unmanned space vehicles from Mission Control Center Moscow” (PDF). Russian Federal Space Agency. Retrieved September 26, 2011.
^ “Nations Around the World Mark 10th Anniversary of International Space Station” (in English). NASA. November 17, 2008.Archived from the original on December 8, 2015. Accessed on March 6, 2009.
^ Price, Pat (2005). The Backyard Stargazer: An Absolute Beginner’s Guide to Skywatching With and Without a Telescope. Gloucester, MA: Quarry Books. s. 140. ISBN 1-59253-148-2.
^ “Human Space Flight” (in English). NASA. July 2, 2008.Archived from the original on December 21, 2015.
^ “International Space Station Overview”. ShuttlePressKit.com. June 3, 1999.Archived from the original on January 21, 2016. Retrieved February 17, 2009.
^ “Fields of Research”. NASA. June 26, 2007.Archived from the original on March 25, 2008.
^ “Getting on Board”. NASA. June 26, 2007.Archived from the original on December 8, 2007.
^ “ISS Research Program”. NASA. Archived from the original on August 11, 2010. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
^ “We’ve Only Just Begun”. NASA. 26 July 2008.Archived from the original on 16 March 2010. Retrieved March 6, 2009.
^ Gary Kitmacher (2006). Reference Guide to the International Space Station. Canada: Apogee Books. ss. 71–80. ISBN 978-1-894959-34-6. ISSN 1496-6921.
^ “Human Spaceflight and Exploration — European Participating States”. European Space Agency (ESA). 2009.Archived from the original on 24 November 2012. Retrieved January 17, 2009.
^ “ISS Intergovernmental Agreement”. European Space Agency (ESA). 19 April 2009.Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved April 19, 2009.
^ NASA (December 15, 2008). “Current ISS Tracking data”. NASA. Archived from the original on December 25, 2015. Retrieved January 28, 2009.
^ Achenbach, Joel (January 8, 2014). “NASA: International space station operation extended by Obama until at least 2024”. washingtonpost.com. Retrieved January 8, 2014.
^ Clark, Stephen (March 11, 2010). “Space station partners set 2028 as certification goal”. Spaceflight Now. Archived from the original on March 24, 2016. Retrieved June 1, 2011.
^ “Canada’s space station commitment renewed”. CBC News. 29 February 2012.
^ “Memorandum of Understanding Between the National Aeronautics and Space Administration of the United States of America and the Russian Space Agency Concerning Cooperation on the Civil International Space Station”. NASA. January 29, 1998.Archived from the original on December 15, 2015. Retrieved April 19, 2009.
^ Payette, Julie (December 10, 2012). “Research and Diplomacy 350 Kilometers above the Earth: Lessons from the International Space Station”. Science & Diplomacy. 1 (4).
^ “National Space Policy of the United States of America” (PDF). White House; USA Federal government. Archived from the original on June 29, 2016 (PDF). Retrieved July 20, 2011.
^ Worldbook at NASA
^ “Mars500 study overview”. ESA. June 4, 2011. Archived from the original on July 31, 2012. Retrieved July 21, 2017.
^ “Space station may be site for next mock Mars mission”. New Scientist. November 4, 2011. Archived from the original on July 11, 2017. Retrieved July 21, 2017.

Due to the rapid increase in the world population and the rapid depletion of natural resources, it has become necessary to search for new mineral resources. Since the natural resources in the world are not sufficient for the increasing needs, the idea of space mining, an interesting plan, has emerged. Mining studies based on obtaining minerals from asteroids in space are called space mining.
It is estimated that mineral reserves such as copper, tin, zinc, silver, lead and gold, which are the most used in industry and have high economic value, will be exhausted in the next hundred years. Experts think that valuable elements such as platinum and cobalt, whose production is gradually decreasing, should be extracted from asteroids and brought to Earth.
According to research, sending a spacecraft to the nearest 500-ton asteroid and bringing the needed minerals to Earth can take 6 to 10 years. It has been calculated that the cost of obtaining minerals from a single asteroid could be $ 2.6 billion. It is estimated that the yield of minerals such as iron, nickel, titanium, gold, manganese, palladium and tungsten that can be extracted from meteorites with precious metals may reach trillion dollars in the near future. If the mine in a meteorite with dense iron ore is extracted, 2-3 times the annual iron production in the world will be obtained. It is known that the 16 Psyche (Sayki) meteorites detected by NASA have enough iron to meet the majority of the iron need of the Earth.
It is thought that the transportation cost of the mines to be brought from space will be quite high. Companies produce various projects in order to reduce the cost in space mining. To these projects; These are examples of sending robots to asteroids and bringing more than a few tons of minerals, developing a different system that will bring small-sized asteroids to Earth, or processing the mine in spacecraft with spaceships.
Although realizing space mining projects is difficult and costly today, it is predicted that this sector may reach trillion dollars in the near future.
Stay with science and knowledge.
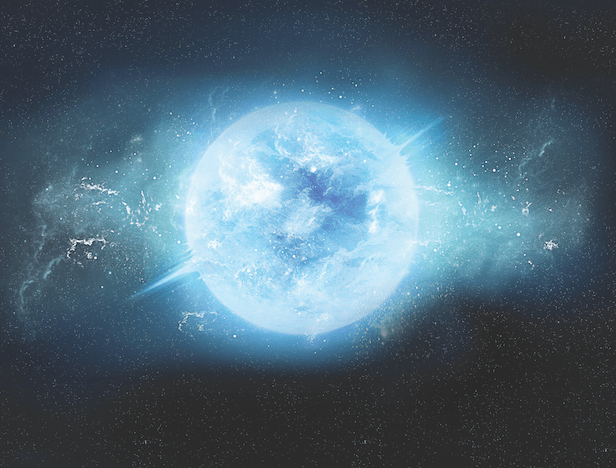

When a high voltage is applied to a handful of aluminum balls in a container; A stylish “dance” emerges in which the particles rearrange themselves in a different “crystal” order. This behavior; It belongs to the phenomenon known as Wigner Crystallization, in which particles with the same electric charge repel each other to form an ordered structure.
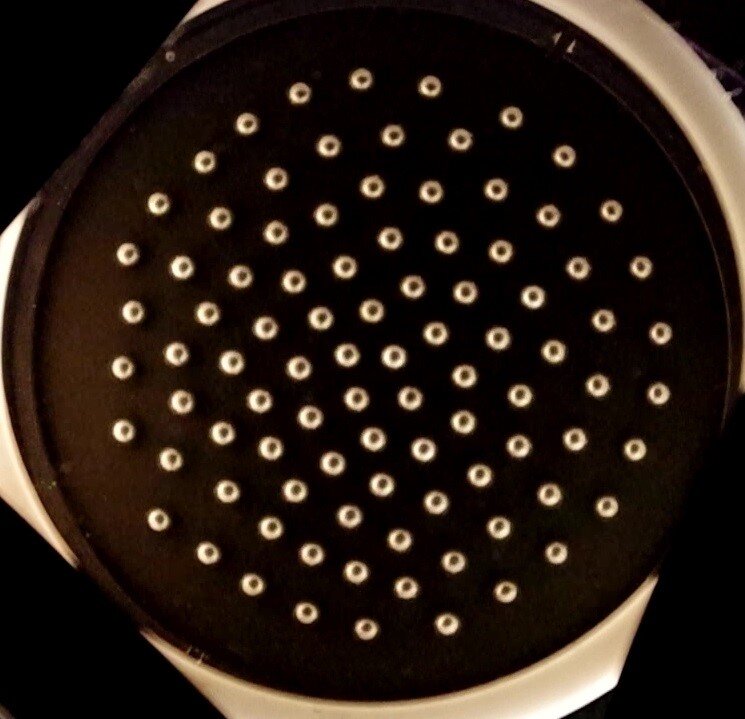
Wigner Crystallization has been observed in various systems, from the size of dust particles suspended in small electron and ion clouds, to the interiors of dense stars known as suspended white sand bodies from particles (called a dusty plasma). Professor Alex Bataller of North Carolina State University recently discovered that Wigner Crystallization within white dwarfs can be studied in the lab using a new class of classical systems called Gravity Crystals.
In order for this behavior of the Wigner Crystallization to occur, it consists of charged particles that are both free to move (plasma), strongly interact with each other (strongly bound particles) and have the presence of a confining force (to prevent the plasma particles from exploding propellantly away from each other). system should be.
To examine this situation for small scales in the lab, Dr. Bataller; He made a new arrangement that puts metal spheres in contact with a high-voltage surface, transferring hundreds of millions of electrons to their surface to charge the spheres, thereby increasing the particle. (Holds the thrust and the particles it contains) Additionally; When the spheres roll over the surface, their motion produces friction that rapidly reduces kinetic energy and promotes strong pairing.
The insight that made the current discovery possible was to use gravity as the limiting force. In this way, small charged spheres can be constrained by gravity using a simple geometry, a bowl.

Using gravitational confinement, Dr. Bataller discovered that Wigner crystallization could now be extended to macroscopic sizes with particles a million times larger than its powdered plasma cousin that could be used to study other crystal systems. For example, gravitational crystals can mimic an interesting feature of white dwarf stars called sedimentation. It has recently been discovered that layered crystal layers can form within white dwarf stars containing oxygen and carbon, where heavier oxygen “sinks” into the core. Gravity crystal arrangement; This produces the layering effect when high voltage is applied to the system of initially mixed copper and aluminum balls. Similar to sedimentation in white dwarf stars, copper balls are drawn towards the center of the bowl, preserving their crystalline structure.
The plasma properties and outer environment of a gravity crystal and a white dwarf star are different from what one can imagine, but both systems exhibit similar behavior, addressing the robust nature of Wigner Crystallization.
Researcher Bataller: The rich diversity in the systems in which we observe the “Wigner Crystallization” is a direct result of its nature independent of its scale. Gravity crystals require the least amount of resources while extending this phenomenon to human resources. What excites me most about this new platform is that anyone that intrigues is able to recreate the state of this fascinating substance, which has been limited to million dollar experiments so far. “
References & Future Readings:
Scitech Daily
Ntboxmag
For additional information see also:
P. E. Tremblay, G. Fontaine, N. P. G. Fusillo, B. H. Dunlap, B. T. Gänsicke, M. A. Hollands, J. Hermes, T. R. Marsh, E. Cukanovaite, and T. Cunningham, Nature 565, 202 (2019).
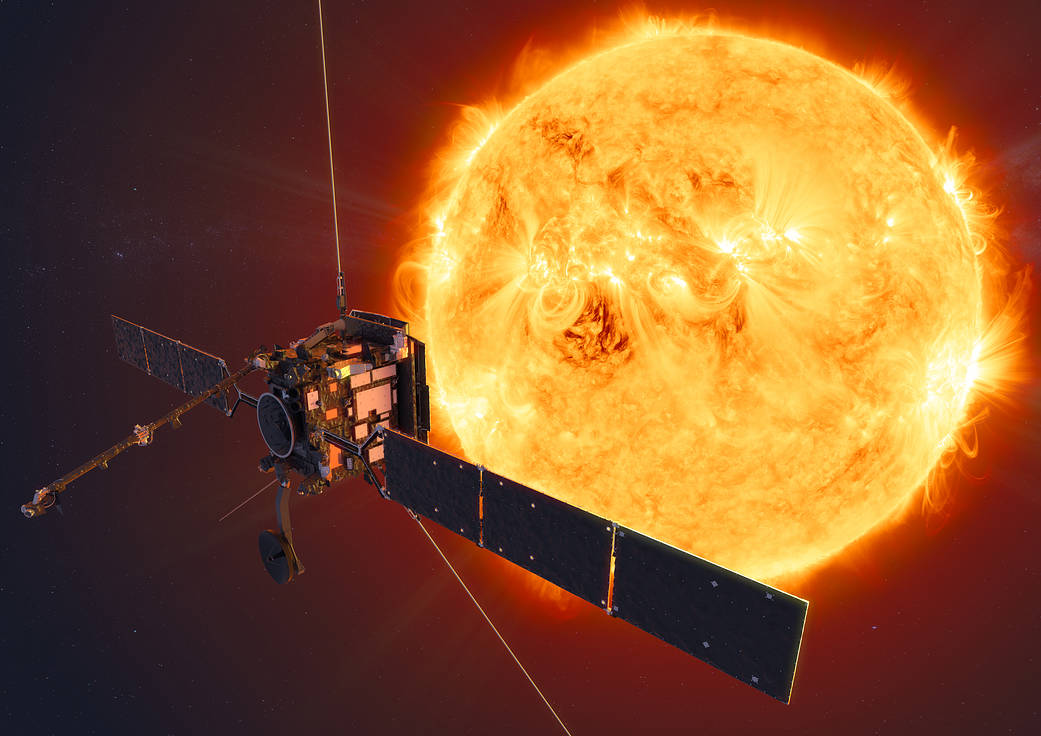

The phenomenon we call solar surfing is desired to be used in many space technologies. As we know, light photons actually have masses at the speed of light because they have a potential force. In this way, they can apply pressure as well as move objects. This phenomenon of moving spacecraft with the power of sunlight is called “solar surf”. This is one of the popular theories that are considered to be applied using sun rays.
Solar Surfing is an early-stage NASA study to support potential future missions that could travel closer to the Sun’s surface than ever before.
Today, NASA and its partners have a fleet of spacecraft studying the Sun. Since launching in 2018, Parker Solar Probe set a record as the closest spacecraft to the Sun. Of great interest to heliophysicists – scientists who study the Sun and its impact on the complex space weather system surrounding Earth, which can impact our technology in space – is the solar transition region, a very thin layer near the Sun’s surface. Parker Solar Probe will come as close as 4 million miles from the Sun’s surface, but spacecraft will need to get to within 500,000 miles to study the transition zone.
In this zone, temperatures start at a “cool” 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit near the Sun’s surface and dramatically increase to about 1.8 million degrees Fahrenheit as you move away from the surface. That is like walking away from a fireplace, and it becomes considerably hotter.
The NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program funds a study by a team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to further research a novel, highly reflective coating for a solar shield that could allow spacecraft to approach the Sun close enough to investigate this exciting region – about 500,000 miles from the surface. The better heliophysicists understand the Sun and how it generates energy, the better they can make predictions of the Sun’s effect on our planet – and improve our everyday communications, electronics, and transportation.
Resources:
NASA
NIAC

The Royal Astronomical Society made a very large and important statement on the morning of September 14, 2020, and announced that they discovered phosphine in the Venusian atmosphere. This is important, because at the level discovered, phosphine (20 molecules per billion) seems to only form if there is “life” as we know it in the environment. Researchers say that non-living sources cannot produce phosphine at this level, or if such a route exists, it is not yet known. This is a very important step towards the hope of finding life outside of Earth.
Chemicals associated with biological elements such as phosphine are called biosignas, and they point to potential life in the environment. This discovery was made with the Atacama (ALMA) telescope array in Chile and the James Clerk Maxwell telescope in Hawaii. Researchers include experts from the University of Manchester, MIT, and Cardiff University. The article was published on September 14 in the journal Nature Astronomy.
Said “sign of life” should not be considered as a complex multi-cellular and systemized structure like human beings. The sign of life in question here is mostly valid for single-celled and simple creatures. An example of phosphine-producing creatures in the world is microbes that live without oxygen. Scientists are excited by the possibility of a sign of extraterrestrial life for the first time, even a microscopic life. However, it should not be forgotten that this phosphine may have been formed as a result of any chemical reaction chain that we do not know yet.
Phosphine (PH3) is a colorless gas that smells like fish or garlic. It boils at -87.7 degrees, freezes at -133 degrees. Inhalation can be fatal, even at very low concentrations. Most of the phosphine is formed by the breakdown of phosphate during the decomposition of organic compounds in the body of living things in an oxygen-free environment. The rest are produced under laboratory conditions. Organisms absorb phosphate minerals, add hydrogen and extract phosphine to produce phosphine. The absence of any oxygen in the Venusian atmosphere makes this gas more likely to come from such microbes.
What makes this discovery important is that the researchers discovered that the amount of phosphine in Venus’ atmosphere is too large to come from abionic sources. If this is the case and there is no error in the measurements, there are two reasonable explanations left:
1) There is an abionic phosphine reaction that we do not know yet, and it is happening on Venus.
2) Or there is life on Venus!
Both of these possibilities are a happy new discovery, a new step for science and humanity.
Resources and Further Reading:
K. Cowing. Phosphine Detected In The Atmosphere Of Venus – An Indicator Of Possible Life ?. (13 September 2020). Date Taken: September 13, 2020. Taken: NASA Watch | Archive Link
J. Roels, et al. (2001). Biological Formation Of Volatile Phosphorus Compounds. Bioresource Technology, pp: 243-250. doi: 10.1016 / S0960-8524 (01) 00032-3. | Archive Link
PubChem. Phosphine. Date Taken: 13 September 2020. Taken from: PubChem | Archive Link
P. S. Anderson. Has Microbial Life Been Found On Venus? | Earthsky.org. (September 12, 2020). Date Taken: September 13, 2020. Taken from: EarthSky | Archive Link
H. Morowitz, et al. (1967). Life In The Clouds Of Venus ?. Nature, pp: 1259-1260. doi: 10.1038 / 2151259a0. | Archive Link
K. Cooper. Could Dark Streaks In Venus’ Clouds Be Microbial Life ?. (05 January 2017). Retrieved: September 13, 2020. Taken: Astrobiology Magazine | Archive Link
K. S. Petersen. How Floating Microbes Could Live In The Acid Clouds Of Venus. (13 August 2020). Date Taken: 13 September 2020. Taken from: Astronomy.com | Archive Link
S. Seager, et al. (2020). The Venusian Lower Atmosphere Haze As A Depot For Desiccated Microbial Life: A Proposed Life Cycle For Persistence Of The Venusian Aerial Biosphere. Astrobiology. doi: 10.1089 / ast.2020.2244. | Archive Link
J. S. Greaves, et al. (2020). Phosphine Gas In The Cloud Decks Of Venus. Nature Astronomy, pp: 1-10. doi: 10.1038 / s41550-020-1174-4. | Archive Link

The age of the universe has been at the center of discussions for quite some time. The universe is only a few thousand years old according to some beliefs, and several million according to some beliefs. In reality, the universe is a much older structure.
Astronomers at the observatory in Chile determined the age of our universe by examining the oldest known light of the universe. Accordingly, our universe has existed for approximately 13 billion 800 million years.
According to two articles published this week in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, researchers were able to determine the age of our universe by examining the cosmic microwave background of the earliest observable light in the universe.
The team of 140 researchers was continuing to work in 41 institutes from 7 countries. The research was led by Princeton University. The data used in the study came from the Atacama Cosmology Telescope in the Atacama Desert in Chile.
The cosmic microwave background is portrayed as the glare believed to have left behind after the Big Bang. The Big Bang is cited by scientific circles as the best explanation for how the universe began. The data obtained by the researchers are also in line with the data received from the European Space Research Organization’s Planck satellite in 2015.
To determine the age of the universe, the researchers looked at light patterns in an area measuring 20 billion light-years that emerged 380,000 years after the Big Bang. One of the two articles with these reviews included sky maps and methodology, while the other focused on the results.
According to the measurements of ACT researchers, an object located one megaparsec, or 3.26 million light-years from the earth, is moving away at a speed of 67.5 kilometers per second due to the expansion of the universe. These results correspond exactly to the results obtained by the Planck satellite. Researchers are now creating the “Infant Photo” of our universe with the data they have.

Niel Armstrong
Mark Armstrong, son of Neil Armstrong, who first set foot on the Moon with Apollo 11 on July 20, 1969, said that his father believed in the existence of aliens.
It has been claimed that astronaut Neil Armstrong, who took the first steps on the Moon, who had the words “a small step for a man but a big step for humanity”, believed in an extraterrestrial life. The claimant is Mark Armstrong, 57, who works as a software engineer in Silicon Valley, son of Armstrong.
Saying that Neil Armstrong, who passed away in 2012, never spoke about his religious belief and had no spiritual experience unlike other astronauts, Mark Armstrong said that his father said that “humanity is not alone in the universe.”
Commenting in his father’s memory, Armstrong said, “Once I heard someone asked my father if he believed in extraterrestrial life and he said,” It would be arrogance to not believe. “
Mark Armstrong continued:
“The Apollo program raised humanity’s faith. It inspired a generation who believed in the importance of working hard for a better future. Today when I talk to people from all over the world, I still see evidence of this, they feel part of the Moon landing. I am excited that the return to the moon is now publicly discussed on forums. “
NASA’s Apollo missions to the Moon ignited many conspiracy theories. One of these was the claims that astronauts had found evidence of extraterrestrial life. Supporters of this theory claim that due to the evidence of extraterrestrial life on astronauts’ lunar travels, NASA did not perform manned missions after 1972.
This claim faces the risk of being refuted in the event of the work that the US space agency plans to send the first female and one male astronauts to the Moon under the Artemis Program by 2024.
NASA, together with partners from Australia, Canada, Europe and Japan, plans to establish a sustainable life on the Moon after the manned mission.
Sources:
Sputnik Türkiye
uzay.org