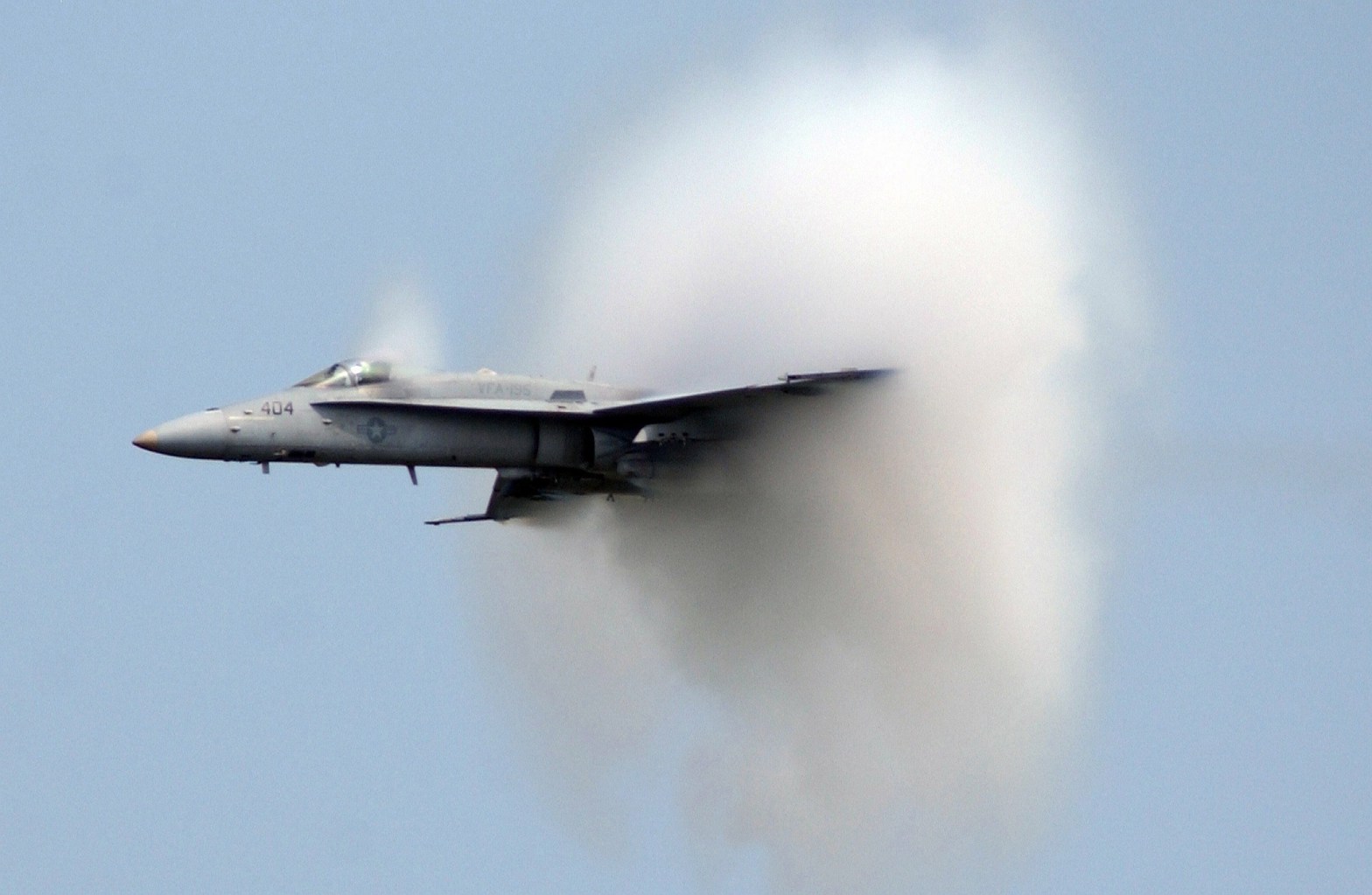
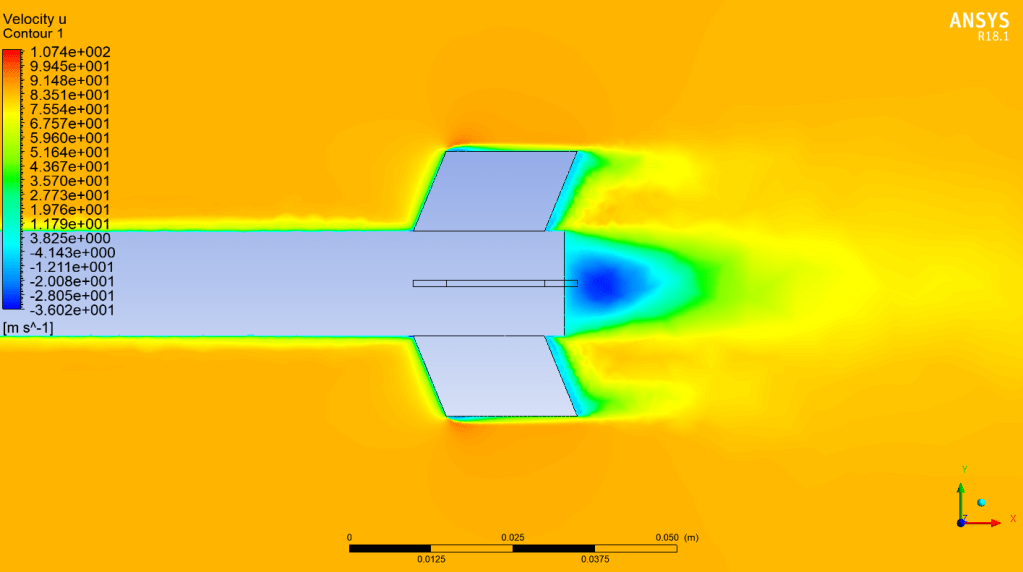
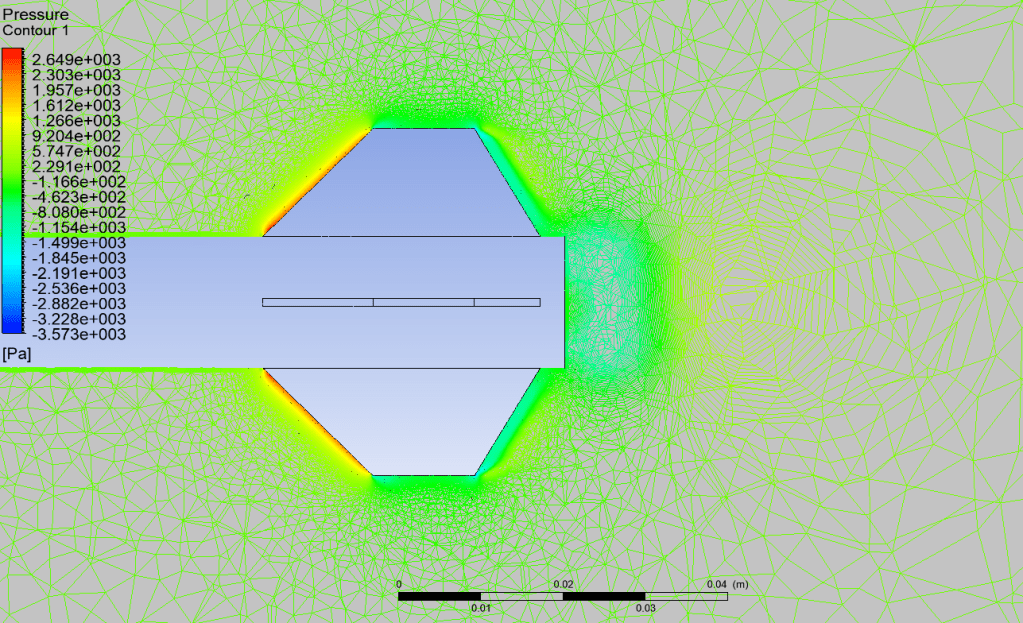
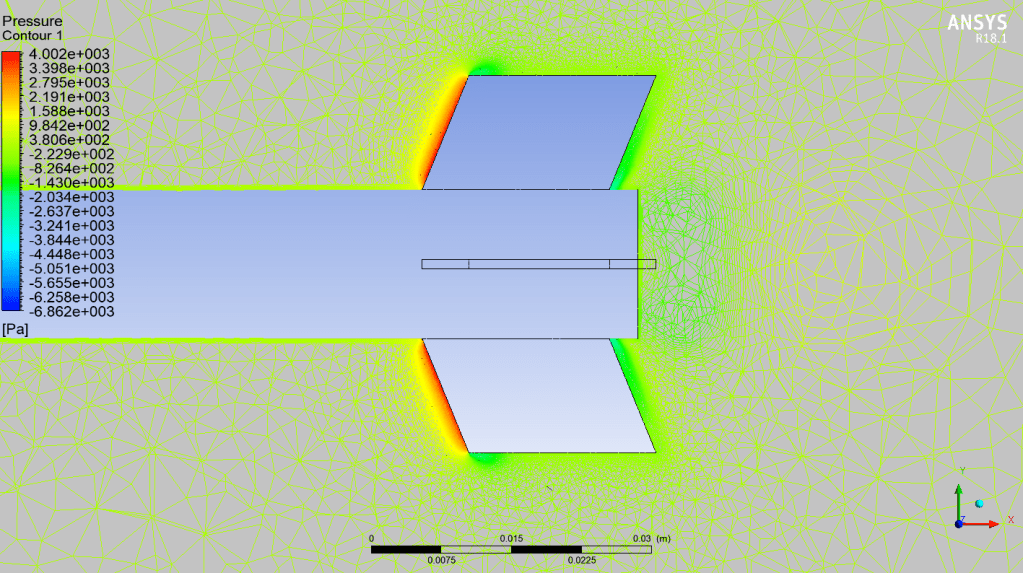
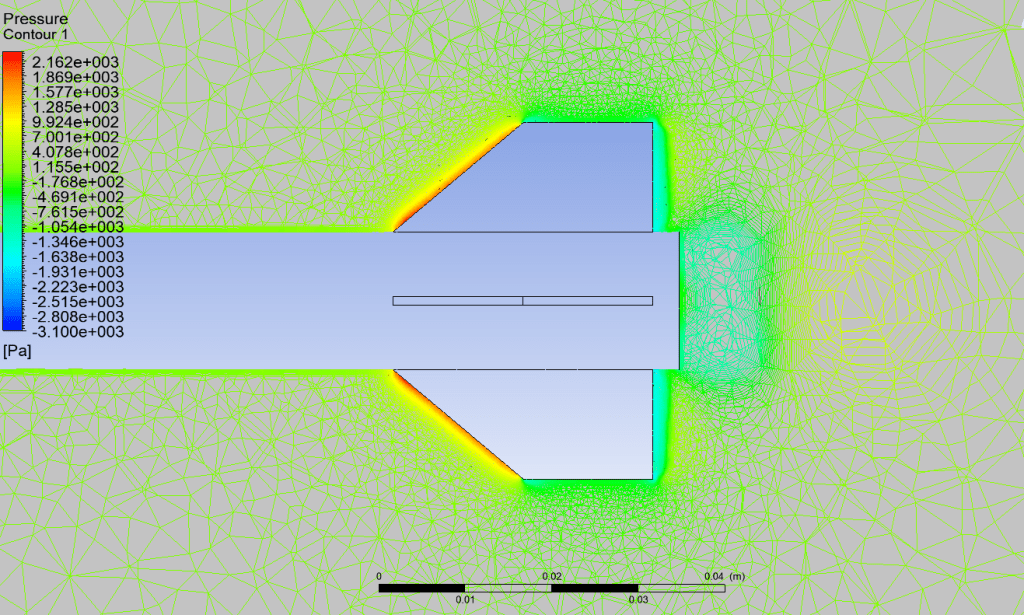
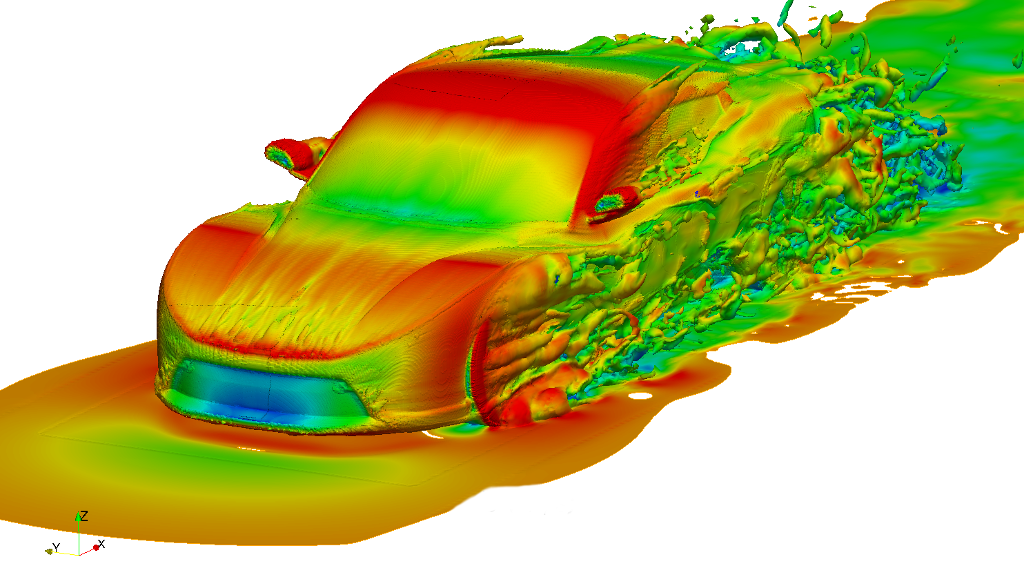
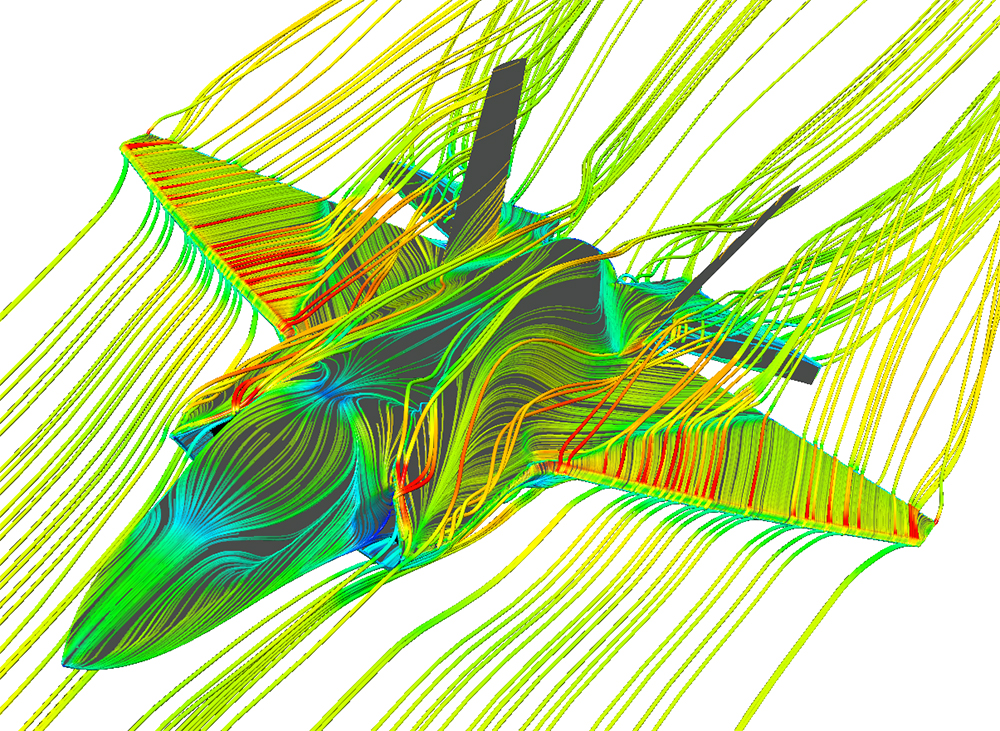
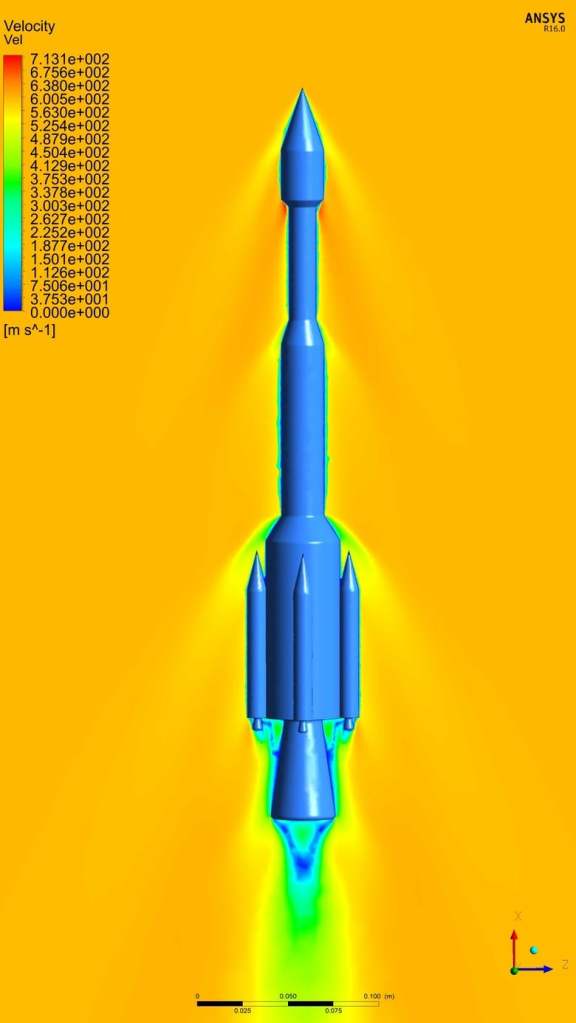
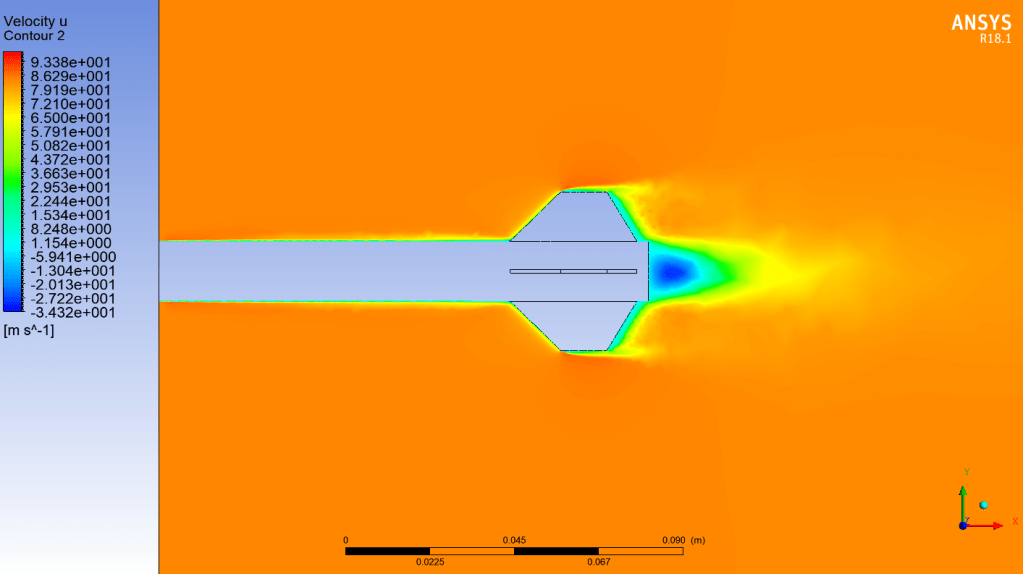
In fluid mechanics, the Mach number is the ratio of the velocity of a moving mass to the speed of sound in the case of the mass. Its abbreviation is Ma or M. It is named after the Austrian physicist and philosopher Ernst Mach. It is also called the Sarrau number from the studies made by the French physicist Sarrau on this subject before Ernst Mach.

The local sound velocity and the Mach number around it are relative to the course of the ambient gases. Mach, first of all. used to be used in a way that is impractically illegible. This medium can be gas or a room. The boundary layer can move through the medium, or move at constant speeds as it flows through the medium, or both at different speeds: performance is at relative speeds that matters. This is the simulation of a channeling tunnel or center of a constrained, possible integrated object. The Mach number is a quantity of dimensions that can be defined as the ratio of two speeds. Mach numbers less than 0.2-0.3 and fully constant and isothermal, reducibility can be applied and simplified non-scalables can be used.
The airway falls from the ground up. The layers of the atmosphere with sea indicators up to 11 km high (as much as the number of Stratosphere) are called the troposphere. From the square of the speed of sound, from the users in the right way with the air, from the speed of sound as it rises. Accordingly, the number of heights is less than the mach sea view.



Importance of Mach Number
First of all, the Mach number gives information about the flow regime. If the Mach number is less than one, it is called subsonic, if it is equal to one, it is called fast (sonic), if it is greater than one, it is called supersonic. It also indicates that the flow is compressible or incompressible as we mentioned before. If M<0.3, the flow is considered incompressible and the density is taken as constant in aerodynamic calculations. On the other hand, when M > 0.3, the flow is said to be compressible.
In the aerodynamic calculations for the compressible and isentropic flow of a calorically perfect fluid, other flow properties can be easily calculated if one of the properties of the flow and the Mach number are known, thanks to the isentropic equations. For example, as shown in the formula below, if the temperature of the fluid at one point and the Mach number are known, the total temperature can be calculated as well as its properties at different points in the flow. These calculations are used in many areas such as the analysis of isentropic regions of the internal flow of a jet engine, especially shock waves.
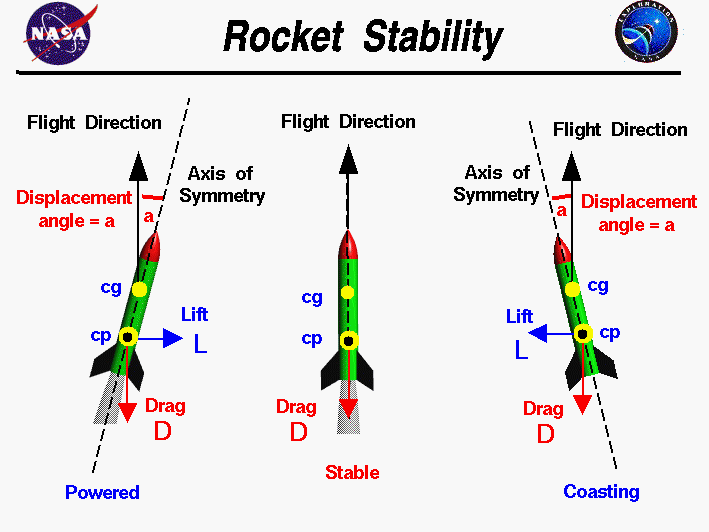
In rocketry calculations and analyses, the mach number tells the awls the conditions we must consider regarding our design. The design suitable for each mach number area makes different requirements essential.
Stay with science and knowledge.
Halit Yusuf Genç
Sources:
Wikipedia
Pixabay
Ucaklar.org